As we all know teeth 🦷 are responsible for breaking down the food into smaller parts for ease in digestion process,
These are classified on the basis of number of sets, shape, shape of cusp, type of attachment, So let’s see in detail,
(1) ON THE BASIS OF NUMBER OF SETS
(a) Monophyodonts
(Only 1 Set)
Eg : Whale, protonema
(b) Diphyodonts
( 2 Sets)
Eg : Man, Apes, Monkeys
(c)Polyphyodonts
( Many sets)
Eg : Fishes
(2) ON THE BASIS OF SHAPE OF TEETH,
(a) Homodonts
all identical teeth.
Eg: Fishes.
(b) Heterodonts
Non identical set of teeth.
Eg : Humans
(3) ON THE BASIS OF SHAPE OF CUSP ( upper surface)
(a) Bunodont ( blunt surface) eg : Humans
(b) Secodent ( Pointy and Sharp) eg : Carnivores
(c) Selenodent ( Criscent Shape) eg : Grazing Animals.
(d) Lophodent ( irregular) eg : Elephants
(4) ON THE BASIS OF ATTACHMENT
(a) Acrodent : Just simply attached or placed on the bones (Alveolar bone)
Eg : Amphibians, Fishes
(b) Plurodont : Attached on one side only, ( loosely)
Eg : Most of the Reptiles
(c) Thicodont : Deeply Placed.
Eg : Humans, Crocodiles, Aligator
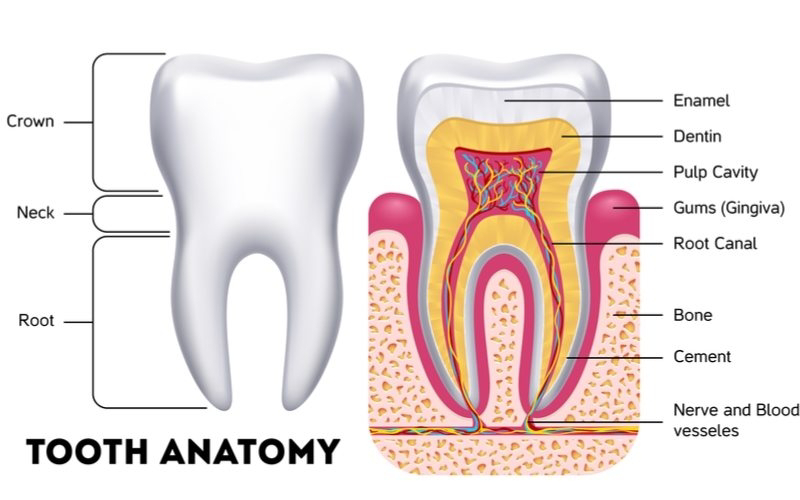
STRUCTURE OF TOOTH